Email deliverability in 2026 is not about sending emails. It is about where those emails land. Many B2B teams think their emails are working because they are delivered. In reality, they have an inbox placement problem. The emails go out, but people never see them.
This guide is for B2B teams that already send emails and want steady inbox placement. It is for founders, marketers, and sales teams who depend on email to drive leads and revenue. These teams follow the rules, yet their emails still miss the inbox.
This checklist shows how email deliverability really works in 2026. It explains what changed and why old advice fails. By the end, you will know what improves inbox placement today and when doing it alone becomes a risk.
Inbox Placement vs Email Delivery: The 2026 Reality Check
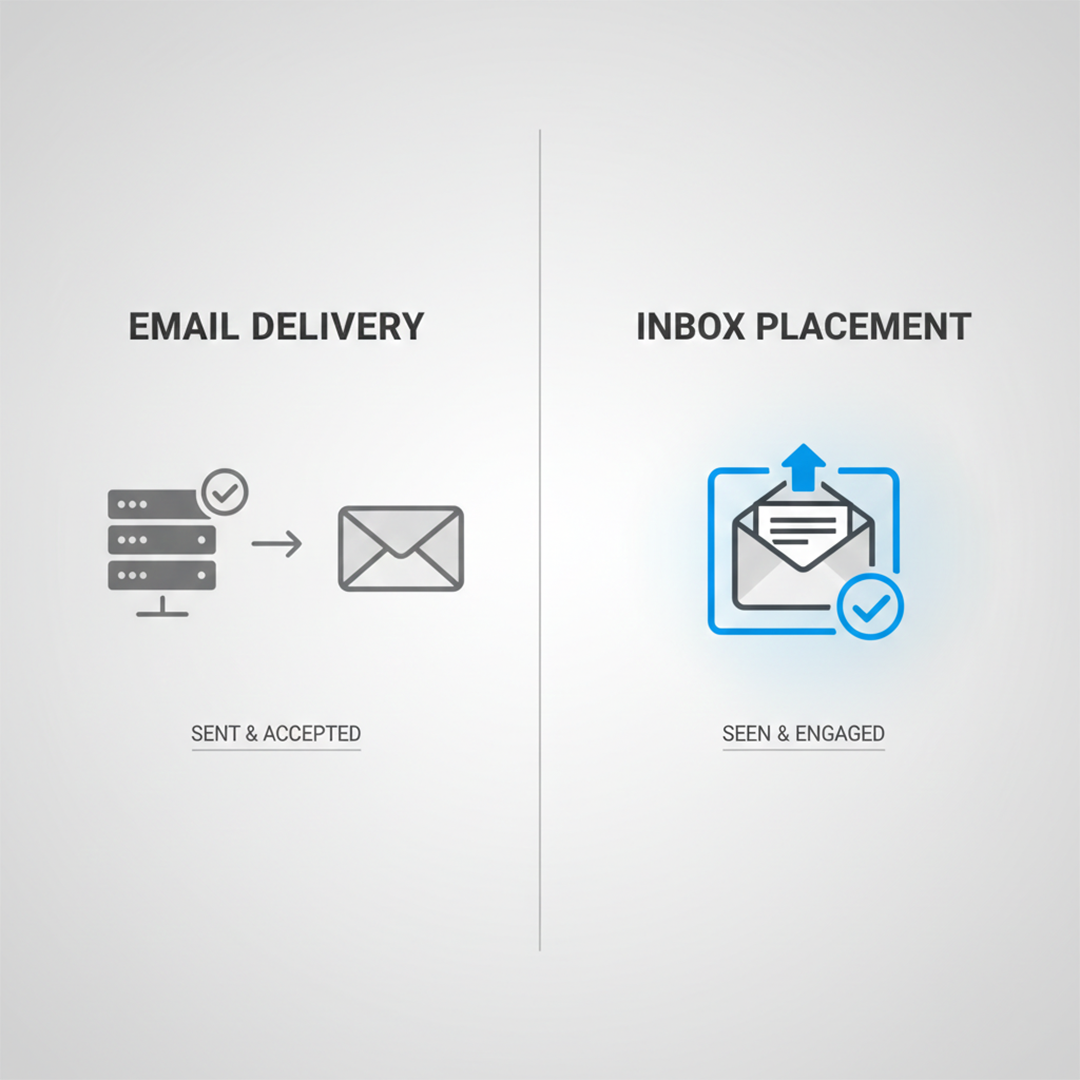
Many B2B teams think their emails are working because the delivery rate looks high. But delivery does not mean the email reached the inbox.
Email delivery is the metric. It shows the mail server message acceptance. On the other hand, Email placement gives you the data about what actually landed in the main inbox.
In 2024, the worldwide inbox placement rate was 83.5%. It means if they sent 6 emails, one of them 1 mail was not reached in the inbox. It might have gone in spam or got filtered out.
Delivery rates can look good, often over 98%, but inbox placement shows the real results.
Inbox placement also changes by email provider. Gmail, Outlook, and other services use strict filters that look at engagement, replies, and sender reputation. Old checklists and simple “send-and-hope” methods do not work anymore.
Many teams follow the basics like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, but still fail. High delivery does not guarantee inbox placement. Today, emails reach the inbox only when engagement, reputation, and provider rules are all in check.
Why Old Email Deliverability Checklists Fail in 2026
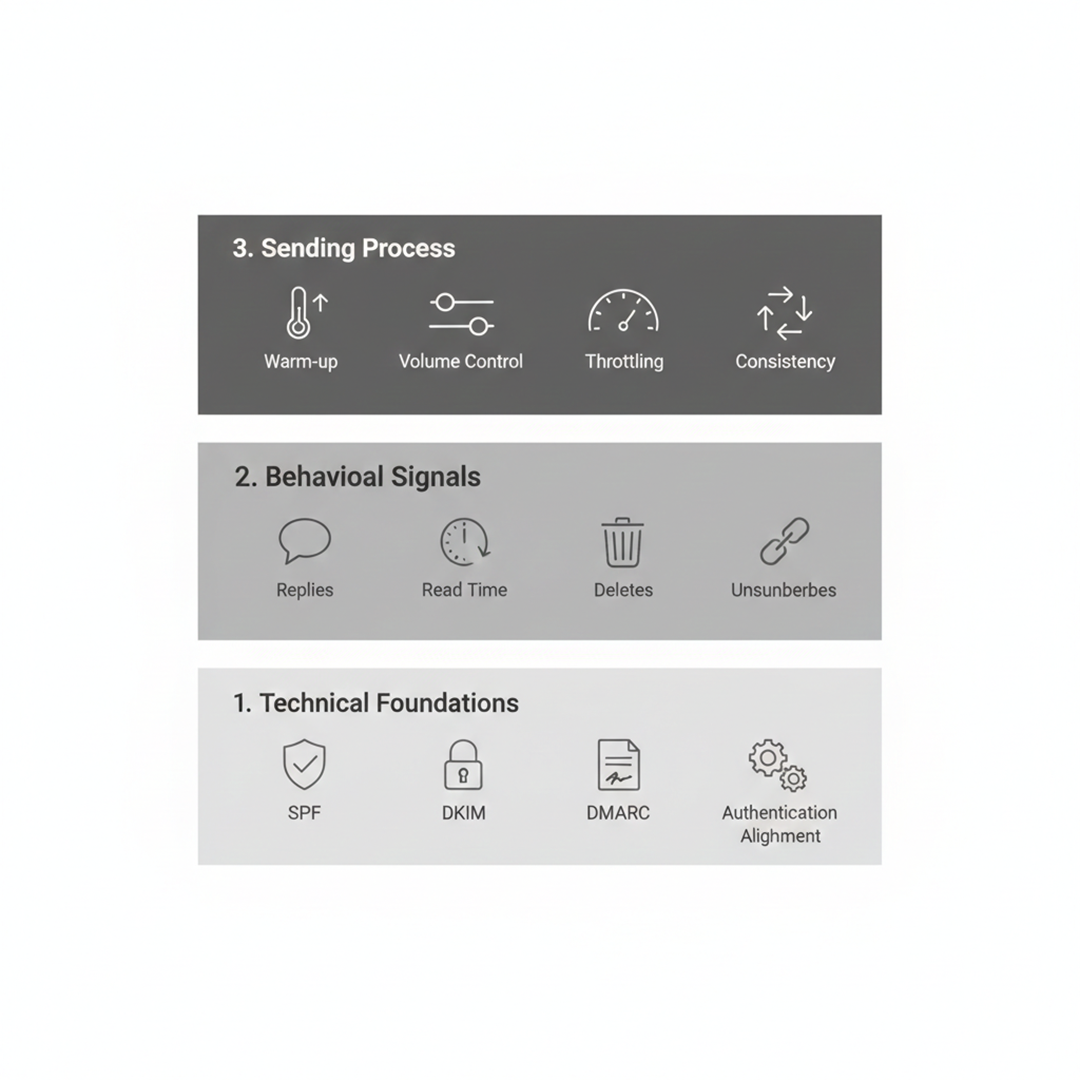
Many B2B teams still use guides from 2022 to 2024. These focus on setup like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. While these are important, they no longer guarantee good email deliverability. Rules for inbox placement have changed fast. What worked a few years ago can fail today.
AI Spam Filters Changed How Emails Are Judged
Spam filters now watch behavior, not just setup. Providers check how people open, reply, and interact with emails. Ignoring these signals can hurt your sender's reputation and push emails to spam. Teams need to focus on spam trigger avoidance and send emails consistently.
Engagement Signals Matter More Than Setup
In traditional Email marketing, always technical setup always gets more priority. But in modern trends, replies, read time, deletes, unscribes, and illigation are more important. High engagement builds up server reputation and trust signals. On the other hand, low engagement can hurt it even if SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are correct.
Inbox Placement Is Now Provider-Specific
There are different types of providers used. Like Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo. They all score email differently. One strategy no longer works well on all platforms. Strategy is very platform-based. Following each provider’s rules is key to getting the best inbox placement in 2026.
The 2026 B2B Email Deliverability Checklist
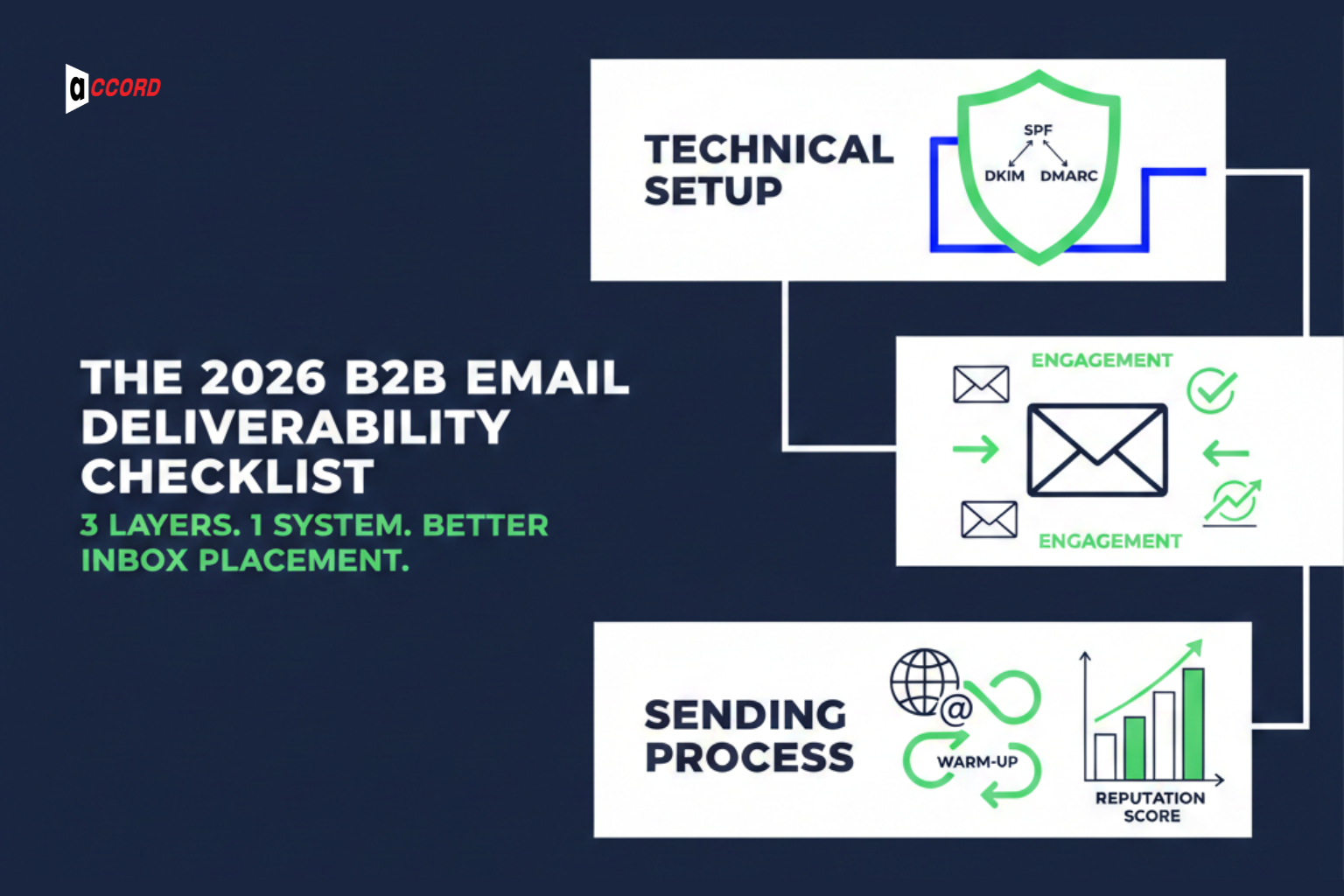
In 2026, good email deliverability is not about one tool or a quick list of steps. Getting emails into the inbox is a system. It works only when three things come together: technical setup, how people engage with your emails, and your sending process.
The technical layer makes sure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are set up correctly. The engagement layer looks at opens, replies, and deletions. The sending process is very important for domain reputation. Email warm-up, sending platforms help to strengthen your domain reputation.
All three layers must work together. When they do, your emails reach the inbox more often. This checklist will show you how to manage each layer and improve email deliverability in a clear and simple way.
Layer 1: Technical Foundations (Email Authentication Alignment)
Before you can get your emails into inboxes, you need to earn basic trust from email providers. This starts with a strong technical setup. Without it, nothing else will work. Even if your emails are well-written and sent at the right time, they may still end up in spam. SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, and proper email authentication alignment form the foundation of good email deliverability.
This layer alone will not guarantee success, but skipping it almost always leads to failure. It shows email providers that your messages are legitimate and not spam. Let’s look closer at how this works.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC Alignment (Not Just Setup)
Setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC is no longer optional. Many teams check the boxes and move on. That is a mistake. These three tools must work together.
-
SPF tells email providers which servers can send emails from your domain.
-
DKIM adds a signature so providers know your emails were not changed in transit.
-
DMARC tells providers what to do if SPF or DKIM fails.
The key is alignment. SPF and DKIM must match your sending domain so DMARC can validate them. Many teams set them up separately, which lowers trust and hurts inbox placement. Common mistakes include missing IPs in SPF or having a DMARC policy that is too weak. When aligned properly, these tools give your emails baseline trust with providers.
Domain vs Subdomain Strategy for Reputation Control
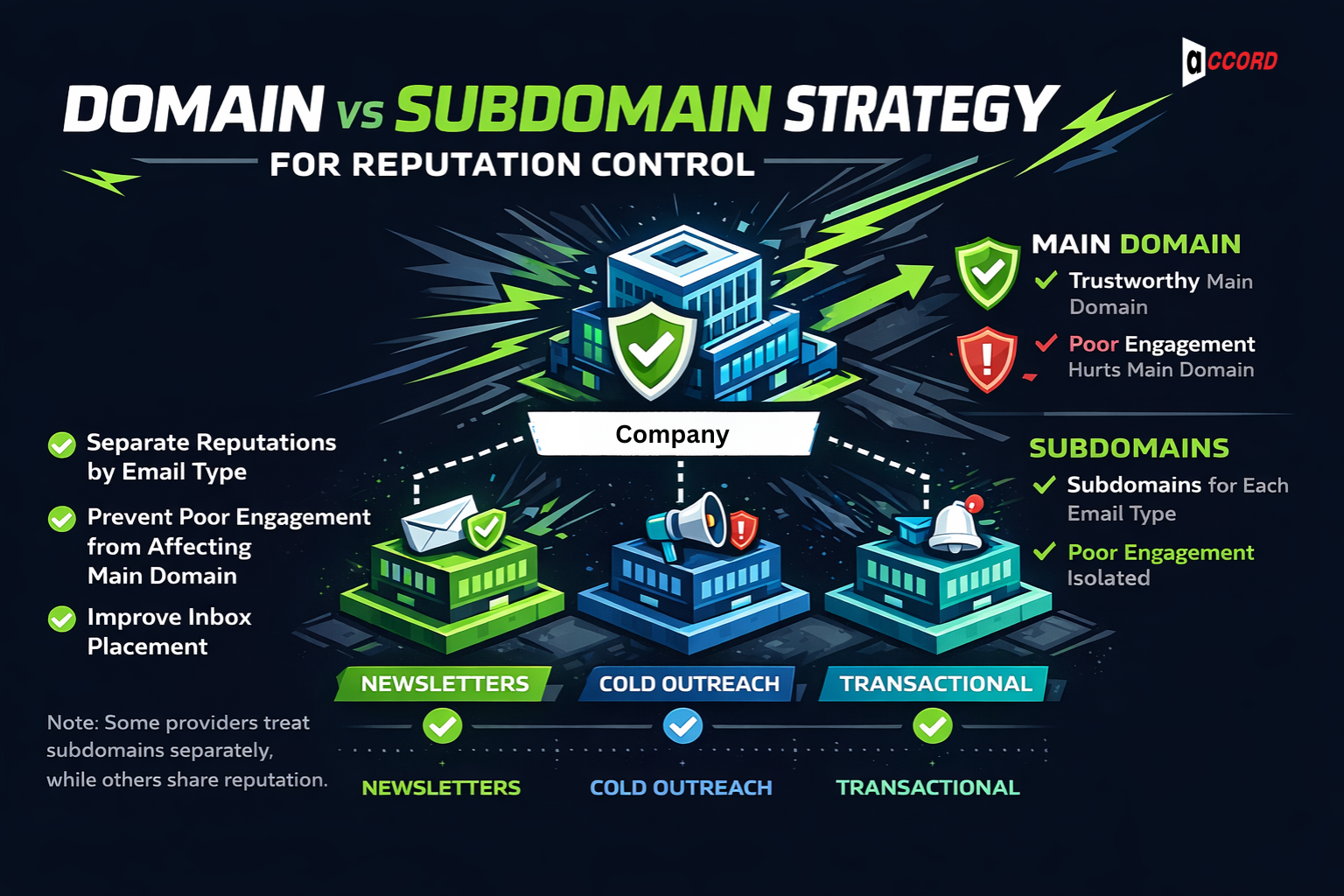
After authentication, you need to protect your sender's reputation. Reputation flows from your sending domain. If one type of email performs poorly, it can hurt all emails from that domain.
A good approach is to use subdomains for different email types. For example:
-
Send newsletters from news.yourcompany.com
-
Cold outreach from outreach.yourcompany.com.
-
alerts.yourcompany.com for transactional notifications
This separates reputations. Poor engagement in one stream does not affect the others.
Some providers treat subdomains separately, while others share reputation. Knowing how your providers work helps you protect your main domain. Managing reputation this way keeps your emails trusted and improves inbox placement.
Additional Trust Signals (BIMI to Briefly)
BIMI, or Brand Indicators for Message Identification, lets your brand logo appear next to your emails in the inbox. It helps build sender reputation by showing recipients that your emails are real and trustworthy.
BIMI is useful, but it is not a fix-all. It does not remove SPF, DKIM, or DMARC. Try to use an extra layer to make your emails look professional and reliable. With strong verification and good engagement, BIMI helps your email get a small boost in inbox placement.
Layer 2: Behavioral Signals That Control Inbox Placement
In this layer, you learn how equally emails land in the inbox. Many teams focus on technical setup but ignore behavior. This is the biggest gap in most guides. In 2026, inbox placement is earned.
Behavior affects sender reputation. Even a perfectly set-up email can fail if recipients don’t engage. Let’s look at the key behaviors that matter.
Reply Rate and Read Time as Inbox Signals
Mailbox providers watch more than opens. They track replies and how long someone reads your email.
Think of it like this: providers ask, “Do people interact with this sender?” If yes, your emails get trusted. If not, they risk going to spam. Encourage replies and engagement in every email.
Delete-Without-Open and Inactivity Penalties
Even if no one marks your email as spam, bad signals matter. Emails that are deleted without being opened or long periods of inactivity can hurt inbox placement.
Your sender reputation drops, and future emails may go to spam. Avoid these mistakes by sending relevant emails and keeping your audience interested.
Managing Unsubscribe and Complaint Rates

An email list health check plays a key role in email marketing. You can check it differently. Unsubscribe and complaint rates are most important. It shows how healthy is list is. Simple mistakes can damage your domain reputation. Keep complaints below 0.1%. And always manage unsubscribe.
High unsubscribe rates indicate that your users do not want your emails. It can push email into spam. Analyze these numbers, and improve content, frequency, or retarget the users.
Layer 3: Email Warm-Up, Volume Control, and Sending Process
Sometimes with a perfect setup or good email format can break your inbox placement. In 2026, email senders will monitor sending frequency closely. How often you send, how fast you scale, and how consistent you are all affect your sender reputation. Skipping this step can undo all your work from the first two layers.
Email Warm-Up and Domain Warming Strategy (2026 Rules)
Warming up a new domain or email account is slower and stricter now. Sending too many emails too quickly can trigger spam filters and hurt your reputation.
A proper email warm-up starts small. Send emails to your most engaged contacts first. Gradually increase volume over several weeks. Your domain warming strategy should track opens, replies, and engagement. Slow and steady growth builds trust. Rushing sends signals of risk to providers.
Many B2B teams make the mistake of sending hundreds or thousands of emails at once. That approach no longer works. Patience is now part of good email deliverability.
Email Throttling Best Practices for B2B Teams
Scaling emails needs control. Email throttling best practices help prevent spam flags. Set daily sending limits. Spread emails across the day. Avoid big bursts of hundreds or thousands at once.
Throttling keeps your sending natural. Providers see steady behavior as trustworthy. Spikes or irregular patterns hurt the sender's reputation and reduce inbox placement. Managing volume is just as important as good content and technical setup.
If you follow this checklist and still hit spam, the problem is usually reputation, not setup. Every layer matters, but how you send emails often decides success.
Get a free inbox placement audit to check your emails and protect your sender reputation.
Inbox Placement Rules by Email Provider (2026)
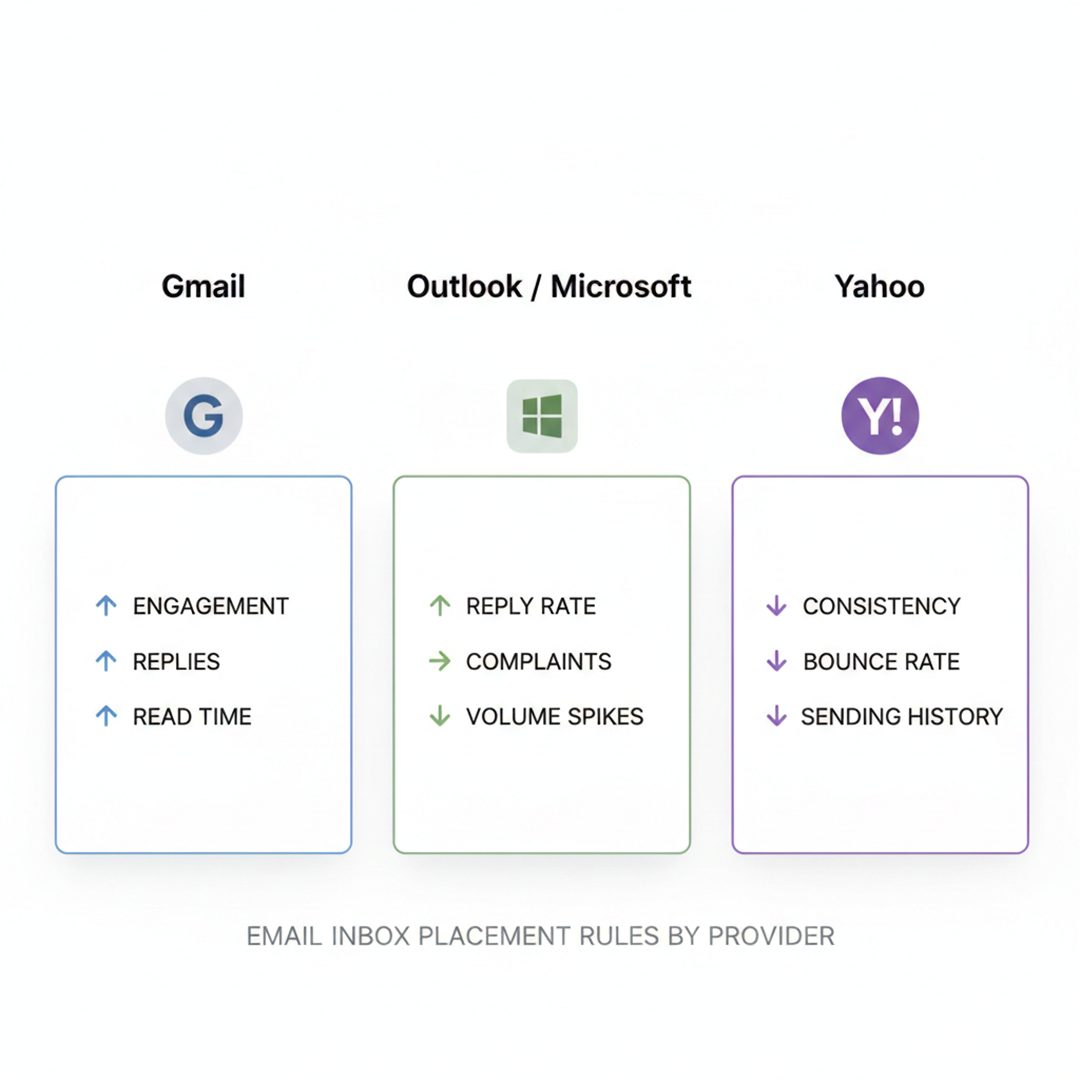
Not all inboxes treat emails the same. In 2026, each provider looks at emails differently. What works for Gmail might fail in Outlook or Yahoo. To improve inbox placement, you need to understand how each provider judges your emails. Recent data shows clear differences in results.
Gmail Inbox Placement Signals
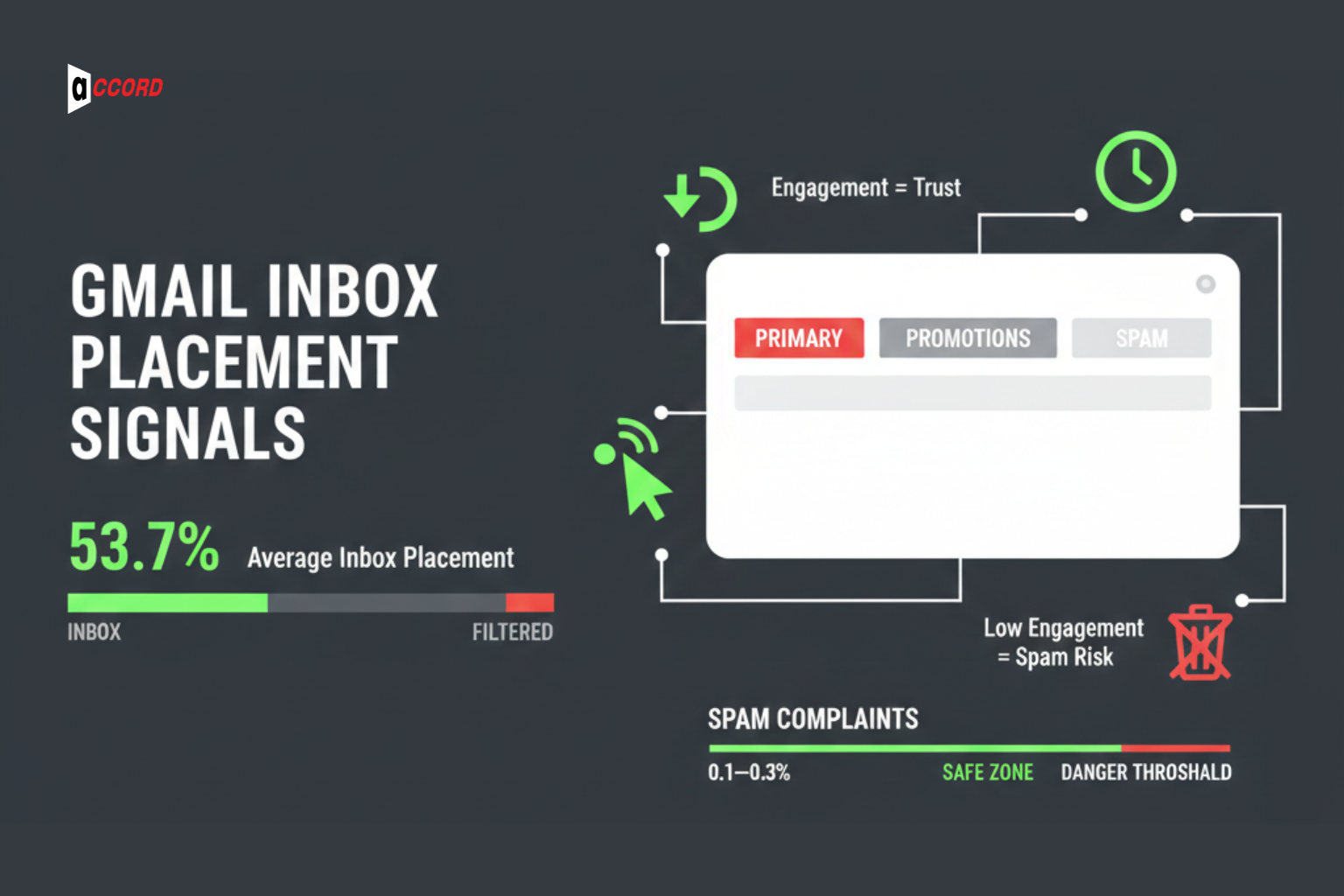
Gmail is one of the busiest inboxes for B2B emails. In 2025, the average inbox placement for Gmail was around 53.7%, meaning almost half of emails might not reach the main inbox if engagement is low.
Gmail cares most about engagement. It tracks replies, clicks, how long someone reads your email, and even if an email is deleted without being opened. Emails with strong replies and read time get trusted more. Low engagement, even with correct SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, can push emails to spam or promotions.
Keeping spam complaints low, under 0.1–0.3%, also helps maintain sender reputation and trust with Gmail.
Outlook / Microsoft Sender Reputation Rules
Microsoft inboxes like Outlook, Hotmail, and Office 365 are strict. In 2025, inbox placement for Outlook/Hotmail dropped to about 26.8%, and Office 365 averaged around 50.7%.
Microsoft looks closely at reply rates, complaints, and sudden volume spikes. Sending too many emails too fast can trigger spam filters. Even fully authenticated emails can go to junk if engagement is poor or sending is inconsistent.
Keeping your sending steady and engagement high is key. This protects your sender reputation and improves inbox chances.
Yahoo Inbox Placement and Volume Sensitivity
Yahoo values consistency and a clean sending history. Its inbox placement averages around 86%, higher than Outlook.
Yahoo looks for steady sending patterns. Sudden spikes or high bounce rates can hurt placement. Low bounce rates, proper authentication, and slow, steady growth keep your emails trusted. Even though Yahoo is forgiving, bad sending habits can still reduce inbox success.
Each inbox scores emails differently. Most B2B teams fail because they treat all providers the same.
See how your emails perform across Gmail and Outlook to spot problems and improve your inbox placement.
Cold Email vs Marketing Email: Different Rules, Different Risks
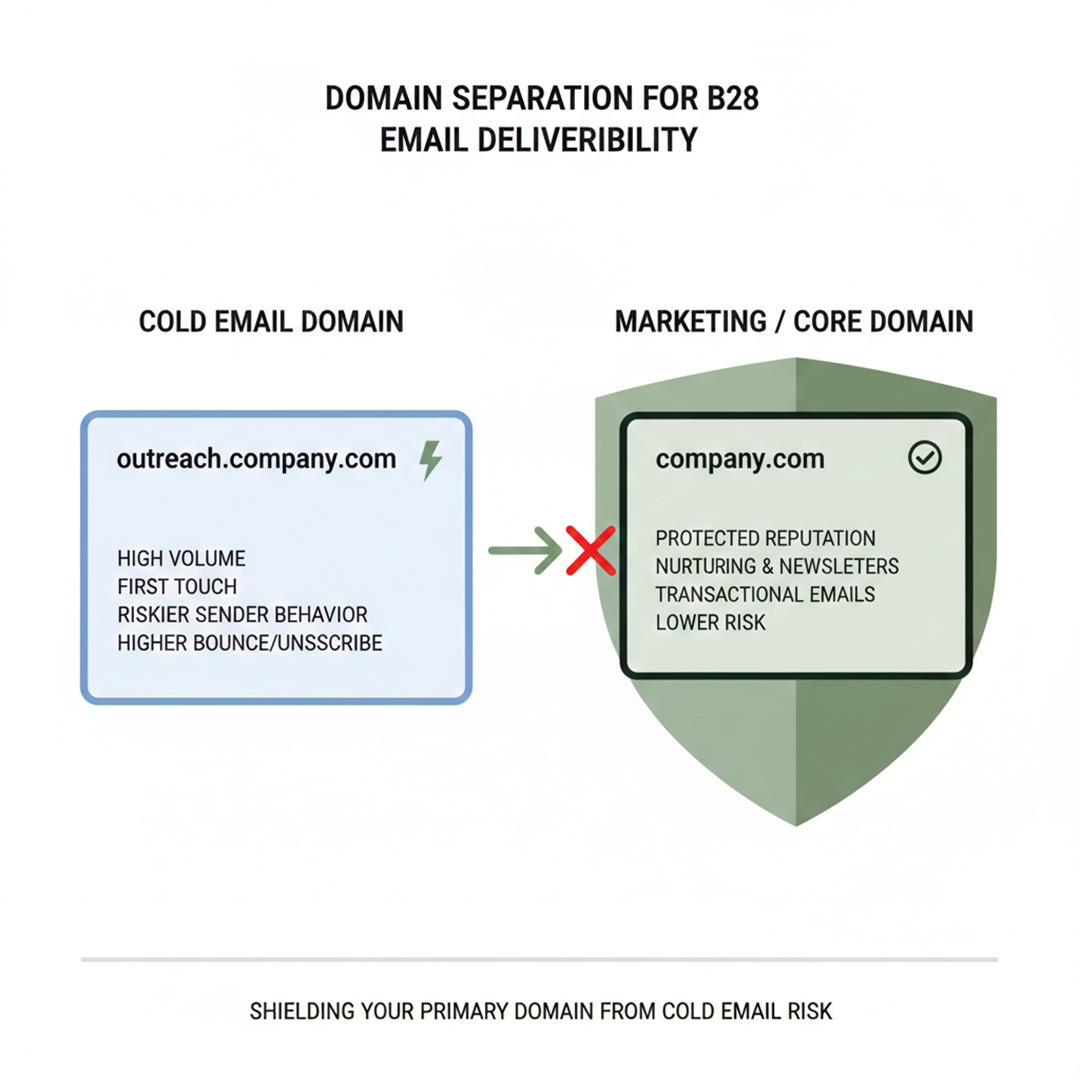
Cold emails and marketing emails follow very different rules for email deliverability. Marketing emails go to people who already know and expect your messages. Cold emails go to new prospects who have never heard from you. This makes cold emails riskier. Even small mistakes can push them to spam or hurt your domain’s reputation.
Why Cold Email Requires Separate Domains
Cold outreach should use a separate domain or subdomain. This protects your main brand domain from damage. If cold emails get complaints or bounce, only the cold domain is affected. Your newsletters and transactional emails stay safe.
A clear domain warming strategy also helps. It builds trust with email providers slowly and keeps your sending reputation strong.
Volume Caps and Warm-Up Discipline for Cold Outreach
Cold emails need slow and steady sending. Sending too many at once is the fastest way to lose inbox placement. Start small, send to your most engaged prospects, and increase volume gradually.
Proper email warm-up tells providers your emails are legitimate. Large spikes or rushing sends can trigger spam filters and damage your reputation. Careful pacing and volume control keep your cold domain safe and ensure your emails land in the inbox.
Using separate domains, warming up slowly, and controlling volume are the keys to safe and effective cold email campaigns. Even technically perfect emails can fail without these steps.
List Quality and Hygiene That Protects Inbox Placement
Even if your emails are perfectly set up, bad data can ruin your email deliverability. In 2026, email providers will watch how clean your lists are. Sending to invalid or risky addresses can hurt your sender reputation faster than poor content or small setup mistakes. High bounce rates and messy lists can undo weeks of careful work. Keeping your lists clean is key to landing in the inbox.
List Hygiene for Email Marketing
In email marketing, list hygiene is regular checking sessions. It helps you remove the unnecessary emails, reduce time-consuming tasks. Here's how it works:
-
Remove invalid email.
-
Delete regular accounts like info@ or support@
-
Nursing and removing inactive or unengaged users
-
Ignore temporary or disposable emails
Detail your contact by activity. Follow up only with people open and engaged. It helps you improve sender reputation. Regular cleaning and filtering keep your campaigns healthy and reliable.
Bounce Rate Reduction and Reputation Protection
Bounces hurt your inbox reputation. Every hard bounce tells providers your email is invalid or unwanted. High bounce rates lower inbox placement and damage sender reputation.
To keep bounces low:
-
Verify new email addresses before sending
-
Remove inactive or unresponsive contacts
-
Avoid buying third-party lists
-
Keep bounce rates below 2% for B2B emails
Low bounce rates mean better deliverability, stronger reputation, and more emails landing in the inbox.
Clean lists and low bounce rates are the foundation of any email campaign. Even the best emails cannot succeed if your list is bad. Focus on list hygiene to protect your domain and improve inbox placement every time.
Common Mistakes That Kill Inbox Placement in 2026
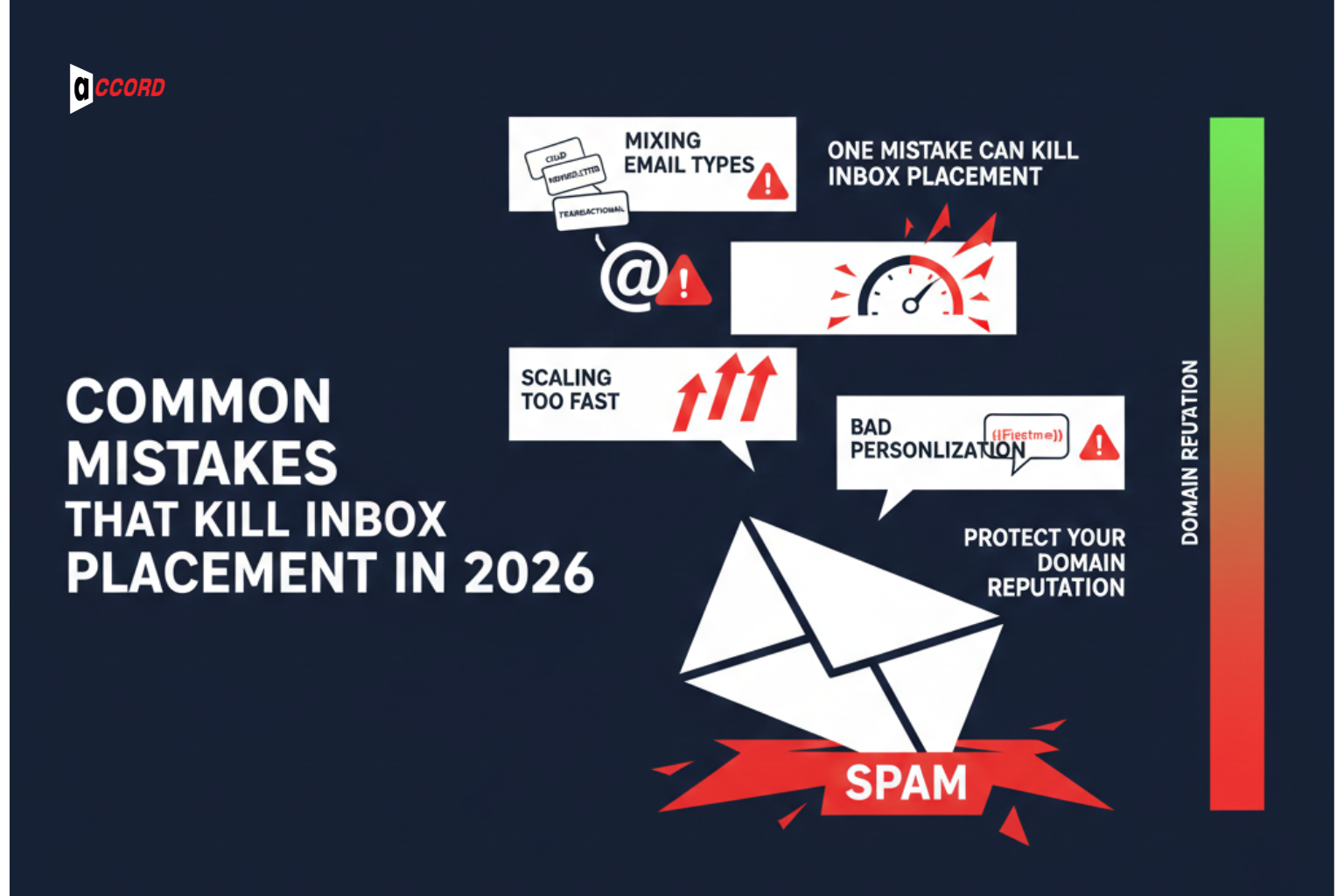
Most of the time, B2B marketers make some common mistakes. These mistakes hurt inbox placement. These impact engagement, damage the sender's reputation. Sometimes put emails in spam. To get rid of it, you have to know about the mistakes and avoid them.
Mixing Cold, Transactional, and Marketing Traffic
There are different types of email formats marketers send. You have to use a specific domain to send a specific email. Sending cold emails, newsletters, and transactional emails in one domain or account always confuses users. This damages the sender's reputation. Keep different types of accounts to protect your main domain and enhance invbox placement.
Scaling Too Fast Without Reputation
In email sending, you have to maintain a perfect flow. Sending too many emails at one time is too risky. Rushing can trigger spam flags, lower placement, and hurt your domain for a long time.
Bad Personalization That Triggers Spam Filters
Shallow or fake personalization can hurt engagement. Using wrong names, repeated phrases, or generic tokens triggers spam trigger avoidance filters. Good personalization shows your emails are relevant. This keeps recipients engaged and protects inbox placement.
One mistake can hurt your domain for months. Small errors in sending, scaling, or personalization can cost deliverability and pipeline opportunities.
We manage deliverability so you don’t risk your pipeline.
Conclusion
Getting better email deliverability and inbox placement in 2026 is more than just setting up SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. You need a clear plan, careful monitoring, and know-how about how providers judge emails.
A simple checklist is not enough. Successful B2B teams combine technical setup, good email behavior, and proper sending practices to land in the inbox every time.
At Accord Tech Solutions, we are more than just an email tool. We act as a deliverability partner for serious B2B teams. We help protect your domain and make sure your emails reach the right audience.
Contact Accord Tech Solutions today to boost your B2B email marketing and get your emails into the inbox consistently.
